ERES: Emergency Response & Evaluation System
📌 Project Overview
ERES is a local-first, high-performance RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipeline designed to transform complex Emergency Operations Plans (EOPs) into actionable intelligence for field responders. The system ingests lengthy, multi-format planning documents and provides instant, grounded answers during active incidents.
The platform bridges the gap between static, PDF-based plans and the real-time information needs of emergency responders operating under high-stress conditions.
🎯 Problem Statement
In Emergency Management, Emergency Operations Plans (EOPs) are critical but cumbersome. Often spanning hundreds of pages, these PDFs are difficult to navigate under the high-stress conditions of an active incident.
Current EOP Limitations:
- Accessibility: Critical information buried in hundreds of pages of documentation
- Search Friction: No effective way to quickly locate specific procedures or contact information
- Visual Data Loss: Maps, organizational charts, and diagrams ignored by standard text extraction
- Time Pressure: Responders need immediate answers when seconds matter
ERES addresses these challenges by providing intelligent document retrieval that preserves both textual and visual information while maintaining complete source accountability.
✨ Key Capabilities
- Visual Preservation: Go-based extractor archives maps, ICS charts, and diagrams for situational awareness
- Layout-Aware Ingest: Sophisticated partitioning understands document hierarchy (headers, sections, tables)
- Fully Local & Private: Designed for air-gapped or sensitive government environments; no data leaves the local machine
- Source Accountability: Every answer includes direct page citations from the original EOP to prevent AI hallucinations
- Dual-Engine Architecture: Separate processing for text and visual data ensures nothing is lost
- High-Performance Retrieval: Optimized vector search for sub-second response times
🏗 High-Level Architecture
The system utilizes a unique dual-engine architecture to ensure both text and visual data are preserved and utilized:
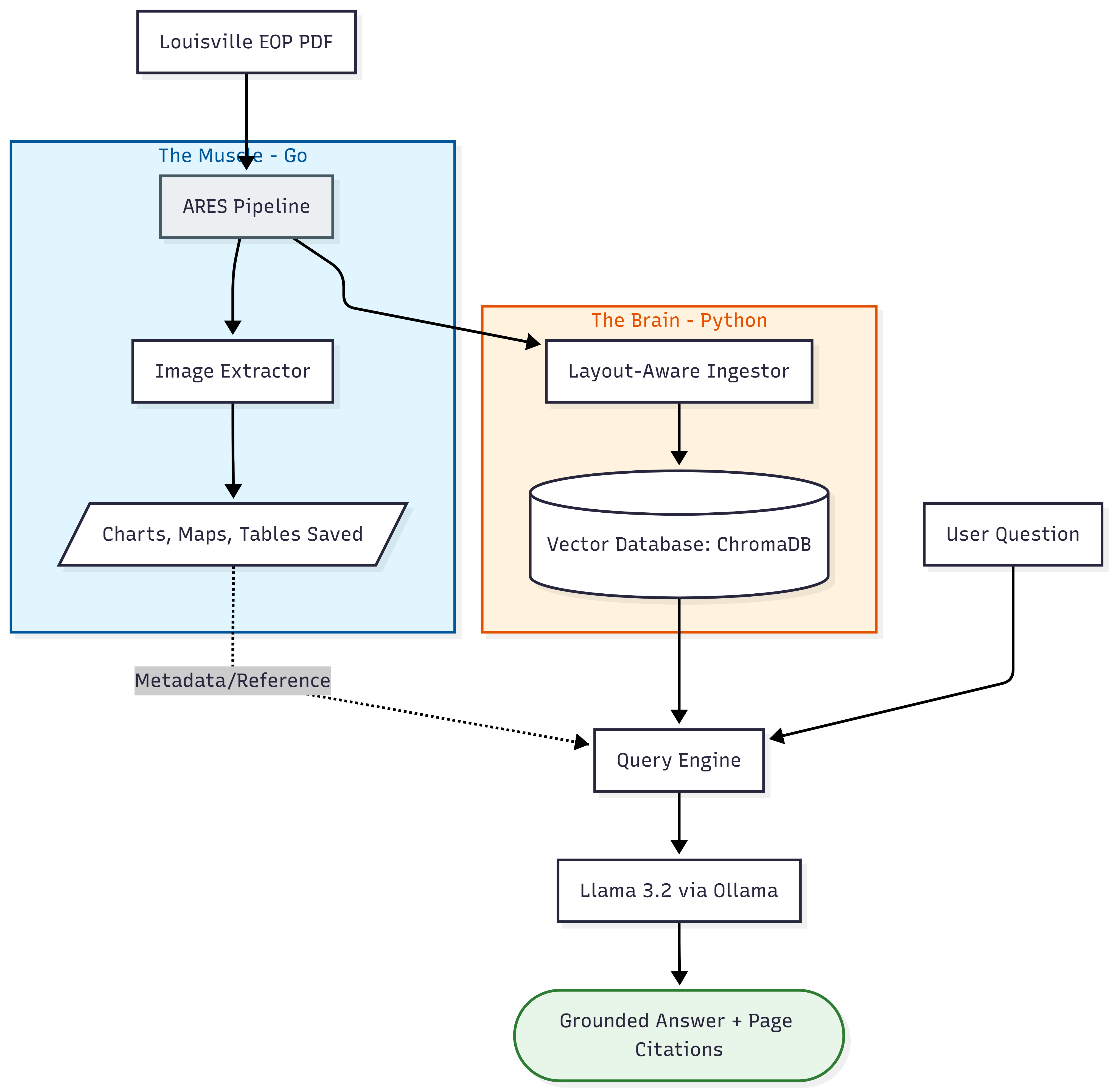
Architectural Principles:
- Extraction Layer: Go-based high-speed PDF parsing with visual asset preservation
- Intelligence Layer: Python-based RAG pipeline with LangChain orchestration
- Retrieval Layer: Vector database for semantic search and embedding storage
- Inference Layer: Local LLM for grounded, citation-backed responses
This design ensures complete information preservation while maintaining privacy and performance requirements for government use cases.
🛠 Tools & Technologies
| Layer | Technology | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Language (Extraction) | Go | High-speed PDF parsing and binary portability |
| Language (AI) | Python 3.12 | LangChain orchestration and data science libraries |
| AI Framework | LangChain | RAG pipeline orchestration and prompt management |
| AI Model | Llama 3.2 (3B) | Local LLM served via Ollama for low-latency inference |
| Vector Database | ChromaDB | High-performance embedding storage and retrieval |
| Model Serving | Ollama | Local model deployment and inference optimization |
| Development | WSL2 (Ubuntu) | Linux-standard development on Windows hardware |
| DevOps | Docker | Containerization for reproducible deployments |
🚀 Future Roadmap: Cloud Scale
Currently transitioning the architecture for event-driven cloud processing:
- Cloud Infrastructure: AWS Lambda for serverless, event-driven document processing
- Storage: S3 bucket triggers for automatic intelligence pipeline activation
- Scalability: Automatic scaling for multi-document and multi-user scenarios
- Monitoring: CloudWatch integration for pipeline observability and performance tracking